A Data-Centric Approach to Analyzing the Skills Gap in Entry-Level Plumbing: Statistical Insights for Education and Training Programs
Skills Gap in Entry-Level Plumbing: Current Landscape
The plumbing industry faces a significant skills gap, particularly among entry-level workers. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, there will be nearly 43,000 job openings for plumbers, pipefitters, and steamfitters each year through 2032, primarily due to retirements and career changes. This highlights the urgent need for skilled new entrants to the field.
The Retention Challenge: Entry-Level Plumbers in the Workforce
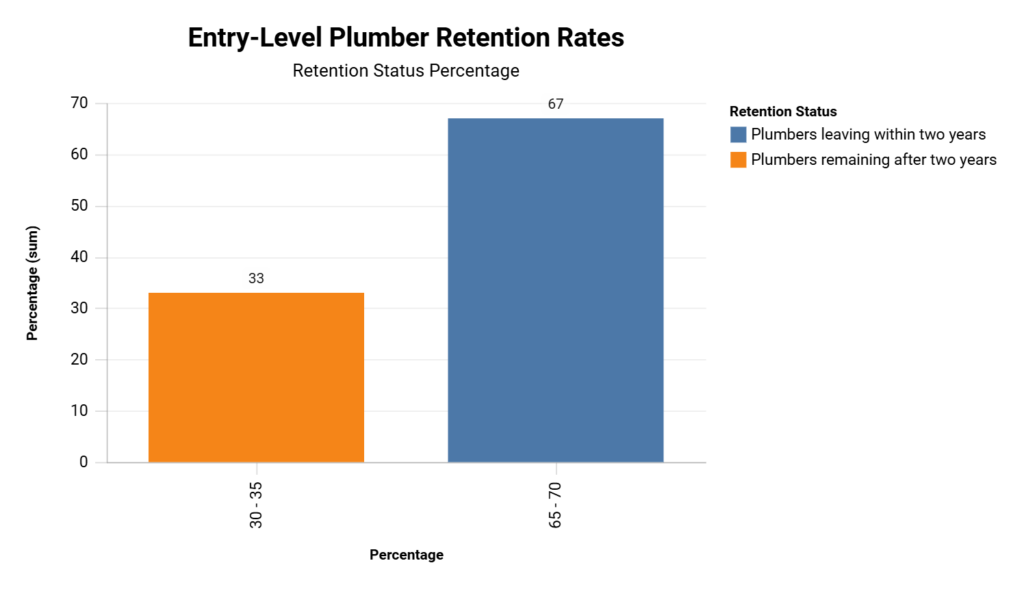
This chart illustrates the significant retention issue facing the plumbing industry for entry-level workers. Only a third of new plumbers remain in the field after two years, highlighting the urgent need for improved retention strategies and support for newcomers to ensure a stable workforce.
Quantifying the Skills Gap
Recent data from Zippia's 2025 workforce analysis reveals that only 33% of plumbers remain in the field for more than two years after entering the profession. This high attrition rate underscores the mismatch between job requirements and the skills of entry-level workers.
Key Areas of Skills Deficiency
Technical Knowledge
Entry-level plumbers often lack comprehensive understanding of modern plumbing systems. The Plumbing Safety Council's 2025 report indicates that 62% of new entrants struggle with interpreting complex blueprints and understanding local codes and regulations.
Technology Adoption
With the increasing integration of smart home systems and sustainable technologies, there's a growing need for tech-savvy plumbers. Plumbing Magazine's 2024 report shows that firms adopting AI-powered diagnostic tools and augmented reality for on-site guidance see a 28% increase in efficiency, yet only 15% of entry-level plumbers feel confident using these technologies.
Soft Skills
According to SendWork's 2024 industry analysis, communication and problem-solving skills are critical for success in plumbing. However, 47% of employers report that entry-level workers lack these essential soft skills.
Education and Training Program Effectiveness
Demographics and Diversity in the Plumbing Industry
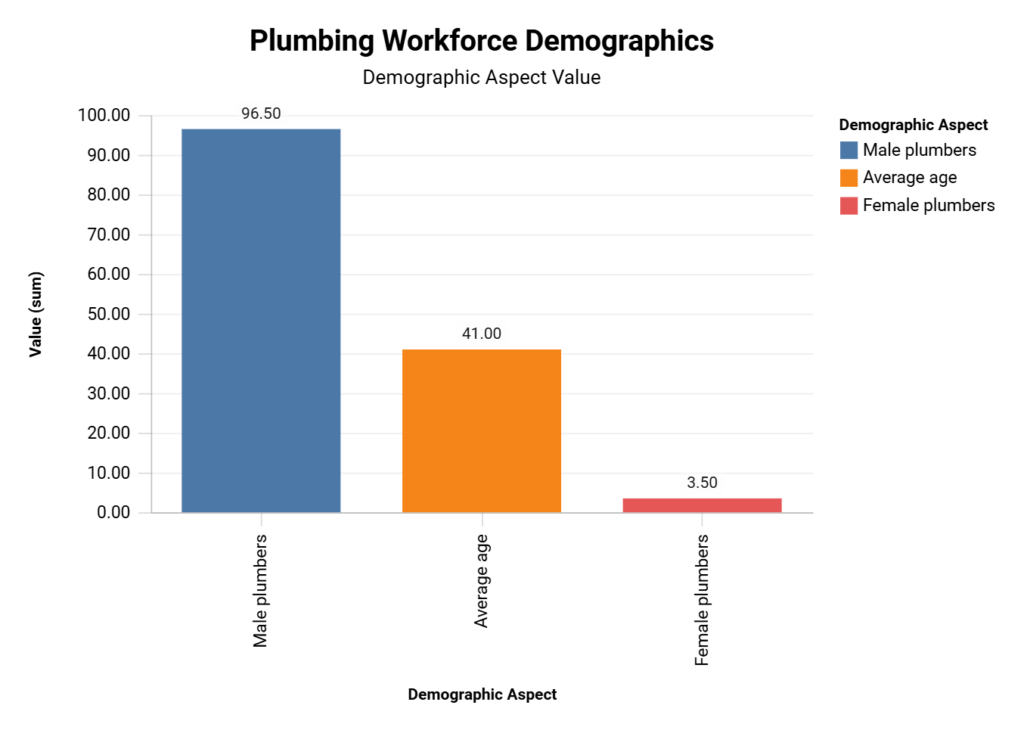
This visualization highlights the current demographic makeup of the plumbing industry, revealing a significant gender disparity and an aging workforce. The data underscores the need for targeted recruitment and retention strategies to diversify and rejuvenate the industry.
Apprenticeship Programs
Data from the National Apprenticeship Tracking System 2024 reveals that plumbers who complete formal apprenticeships are 2.3 times more likely to remain in the field for at least five years compared to those who enter without structured training.
Vocational Training
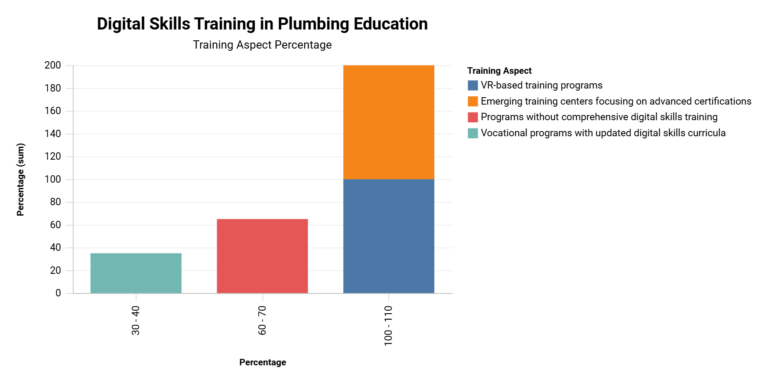
While vocational programs provide theoretical knowledge, there's often a gap in practical application. The Plumbing Business Association's 2024 study shows that only 35% of vocational programs have updated their curricula to include comprehensive digital skills training as of 2025.
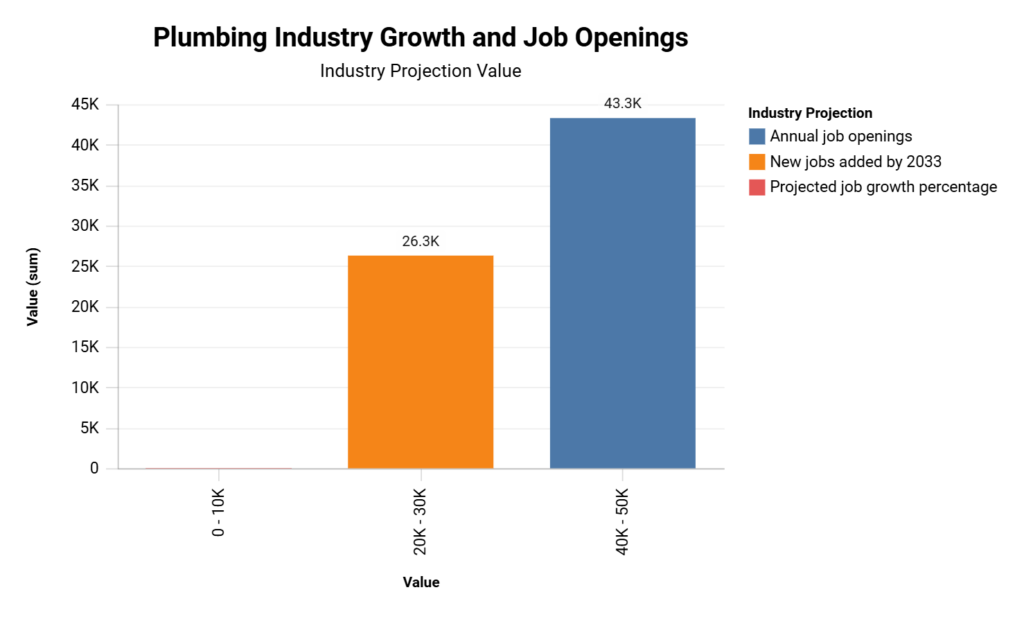
Future Prospects: Job Growth and Openings in Plumbing
This chart presents the projected job growth and annual job openings in the plumbing industry. Despite retention challenges, the sector shows promising growth, with a significant number of job openings expected annually, indicating opportunities for those entering the field.
Strategies for Bridging the Skills Gap
Industry-Education Alignment
Collaboration between industry and educational institutions is crucial. Trojan Plumbing's 2024 report emphasizes the importance of hands-on training and mentorship in fostering the next generation of plumbers.
Technology Integration in Training
PM Magazine's 2025 industry outlook suggests that incorporating advanced technologies in training programs can increase job readiness by up to 40%.
Continuous Learning Programs
The rapidly evolving nature of the plumbing industry necessitates ongoing education. BuildOps' 2023 analysis shows that companies offering continuous learning opportunities have 31% better retention rates among entry-level employees.
Conclusion
Addressing the skills gap in entry-level plumbing requires a multi-faceted approach involving education reform, industry collaboration, and technology integration. By focusing on these areas, the plumbing industry can ensure a skilled workforce capable of meeting future challenges.
For those looking to enter the field or enhance their existing skills, the Fast-Track Tech Career Course offers accelerated 4-16 week programs tailored to the modern plumbing industry. Start your first lesson free and join the ranks of skilled plumbers shaping the future of this essential trade.
Source Data
| Article Title | Publication | Date |
|---|---|---|
| Plumber Demographics and Statistics | Zippia | 04/05/2025 |
| Plumbing Industry Statistics 2025 | Jobber | 01/09/2025 |
| Skills Shortage in Plumbing: The Urgency for Effective Training | Trojan Plumbing | 07/15/2024 |
| Plumbing Programs – BuildOps | BuildOps | 02/08/2023 |
Explore More Plumbing Insights
If you found this review helpful, check out our other plumbing-related articles for deeper insights:
- Data-Driven Analysis of Entry-Level Plumber Retention Rates and Factors Influencing Career Longevity
- Statistical Evaluation of Technology Adoption Among Entry-Level Plumbers: Impact on Job Performance and Career Advancement
- CourseCareers Plumbing Course Review
These articles provide valuable data on career growth, technology adoption, and training strategies for aspiring plumbers.