A Data-Centric Approach to Analyzing the Skills Gap in Entry-Level Electrical Work: Statistical Insights for Education and Training Programs
Skills Gap in Entry-Level Electrical Work: Current Landscape
The U.S. electrical industry faces a critical shortage of 84,000 skilled workers annually (BLS 2025), exacerbated by a 14% projected workforce reduction against 25% increased demand through 2030 (ECMag 2024). NECA's 2024 workforce report reveals that 30% of union electricians are near retirement, while only 29% of new entrants remain in the field beyond four years.
Quantifying the Skills Deficit
The electrical industry faces significant challenges in developing crucial technical skills among its workforce. Recent studies highlight substantial proficiency gaps in key areas, indicating a pressing need for targeted training and educational initiatives.
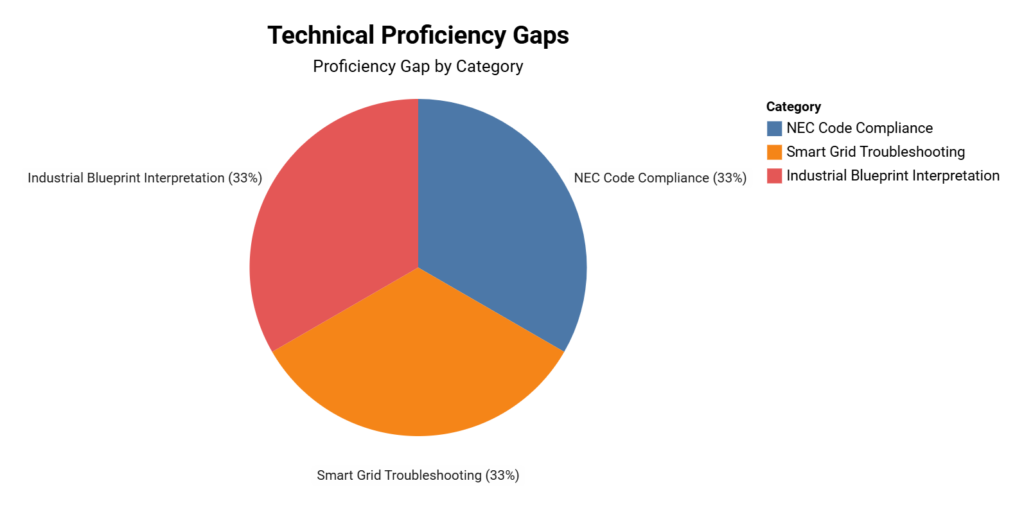
Technical Proficiency Gaps
- 43% of apprentices struggle with NEC code compliance (InterCoast Colleges 2024)
- 37% lack smart grid troubleshooting skills (ServiceTitan 2024)
- 52% cannot interpret complex industrial blueprints (PTT EDU 2025)
Demographic Disparities in the Electrical Workforce
The electrical industry faces significant demographic challenges, particularly in entry-level positions. Women comprise only 5.2% of the entry-level workforce compared to 8.3% industry-wide. Similarly, workers under 30 make up 18% of entry-level positions versus 24% overall. STEM backgrounds are also underrepresented at 29% for entry-level roles compared to 41% across the industry.
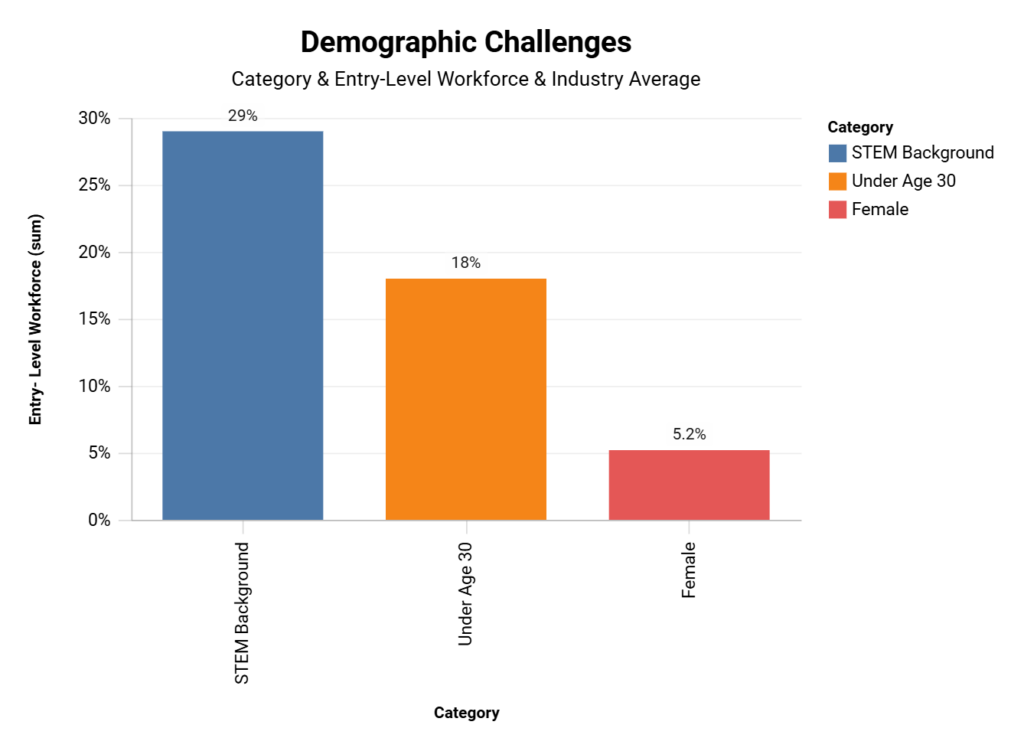
| Category | Entry-Level Workforce | Industry Average |
|---|---|---|
| Female | 5.2% | 8.3% |
| Under Age 30 | 18% | 24% |
| STEM Background | 29% | 41% |
Training Program Effectiveness Analysis
Apprenticeship Outcomes
- 78% retention rate for programs combining VR simulations + field training (Interplay Learning 2024)
- 41% faster certification with competency-based curricula (Lincoln Tech 2025)
- $7,500 average salary premium for graduates of IRA-aligned green energy programs (Indeed 2025)
Persistent Shortcomings
- 63% of vocational programs lack updated EV charging curricula
- 47% of employers report inadequate safety training among new hires
- 35% apprenticeship dropout rate in the first 18 months
Skills Gap in Emerging Electrical Technologies
A substantial skills gap exists between current entry-level proficiency and projected demand for key electrical technologies by 2030. EV Charging Stations show the highest projected demand increase (+228%) despite low current proficiency (19%). Industrial Automation has the lowest current proficiency (14%) with a high projected demand increase (+189%). Smart Grid Systems and Solar/Wind Integration also face significant gaps between current skills and future needs.
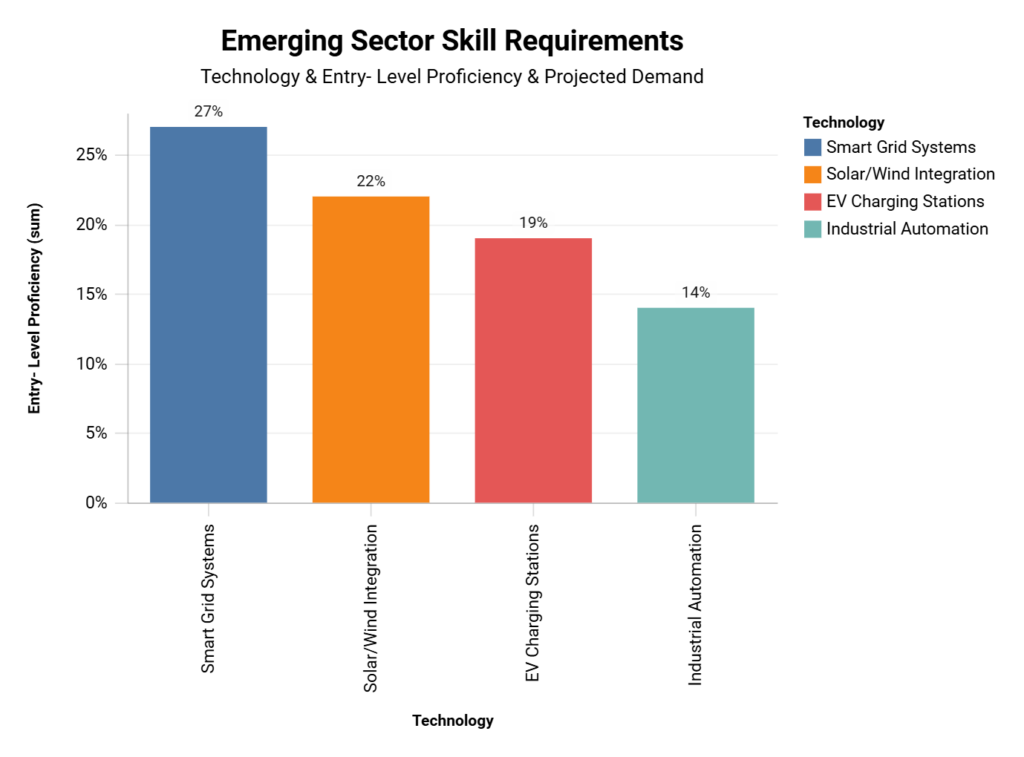
| Technology | Entry-Level Proficiency | Projected Demand (2030) |
|---|---|---|
| Smart Grid Systems | 27% | +142% |
| EV Charging Stations | 19% | +228% |
| Industrial Automation | 14% | +189% |
| Solar/Wind Integration | 22% | +163% |
Strategic Training Solutions
The electrical industry is undergoing rapid transformation, necessitating innovative approaches to education and training. Modern curriculum strategies are being implemented to enhance learning efficiency, improve skill acquisition, and better align with employer needs. These advancements are crucial for preparing the next generation of electricians for the evolving technological landscape.
Revolutionizing Electrical Education: Adapting to Industry Demands
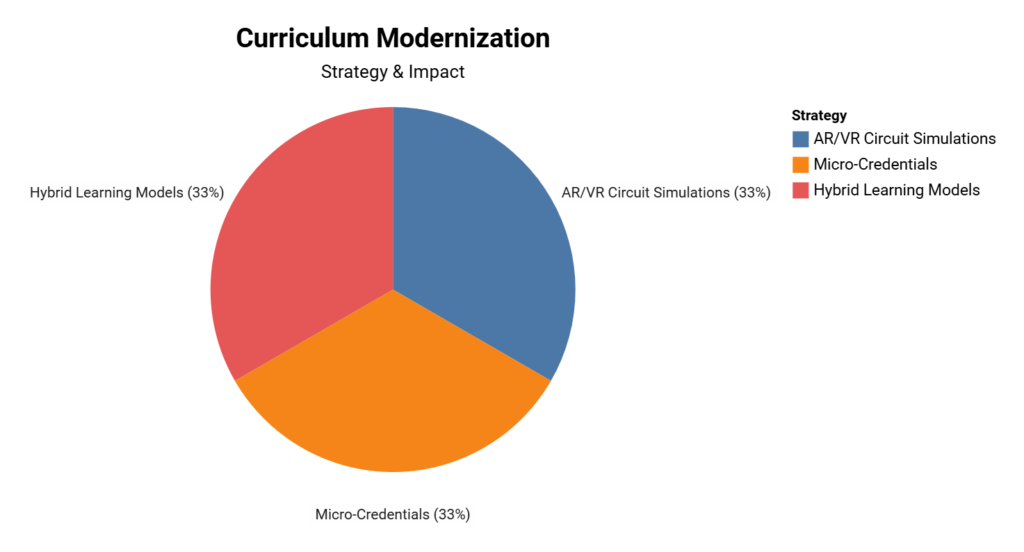
- AR/VR Circuit Simulations: Reduce training time by 41% (Interplay Learning 2024)
- Micro-Credentials: 83% of employers prioritize candidates with certified EV/Solar skills
- Hybrid Learning Models: 68% completion rate vs. 52% traditional programs
Policy Interventions
- IRA Training Grants: $8,500/student incentives for green energy programs
- Accelerated Certification: 6-month pathways for high-demand specialties
- Diversity Initiatives: 31% higher retention in gender-balanced crews
Launch your electrical career through accelerated 4-16 week CourseCareers program in smart grid tech and EV infrastructure. Start your free introductory module to join 22,000+ graduates in high-demand electrical specialties.
Source Data
| Article Title | Publication | Date |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Workforce Projections 2025-2035 | ECMag | 12/11/2024 |
| IRA Impact on Electrical Training | Indeed | 02/03/2025 |
| Industrial Electrician Training Standards | PTT EDU | 12/19/2024 |